Testing sites and web applications across platforms, devices, and browsers has become one of the cornerstones of quality assurance. An online web browser emulator is the essential tool that enables developers and QA engineers to replicate how websites look and function in different environments without owning every possible device or operating system.This guide ventures into defining a web browser emulator, how it works, why it is essential, and the different types of emulators available. We will also review popular browser emulator online services and highlight their role in streamlining modern web testing.
Meaning and understanding of a browser emulator
Different communities often have different interpretations of the term browser emulator. In its widely accepted meaning, a web-browser emulator is an online service that emulates a real browser’s behavior. This is often achieved by opening a virtual copy of the browser environment or simply giving the user remote access to a real-time instance of the browser. Testing platforms in a professional setting within the context of web development is precisely what is meant when the term online web browser emulator is used. This will be the interpretation applied to this term throughout the article.
In a broader sense, a web emulator might translate to something attendant to software or service that simulates an evenly functioning system within a browser window. For example, an iOS or Android browser emulator gives the mobile operating system environment within the browser itself, so that developers can preview apps and websites as they would appear on those platforms. Retro-gamers may also make use of browser-emulator services to run ROMs for some of their classic consoles (like NES or PS1) right in the same browser window.
This means the meaning is not universally understood, it largely depends on whether we refer to a professional QA context or something else like system emulation or maybe even a computer game. For the sake of clarity, the article considers the QA use case in which the browser emulator actually emulates real browser behavior to test websites and applications.
How a Browser Emulator Works
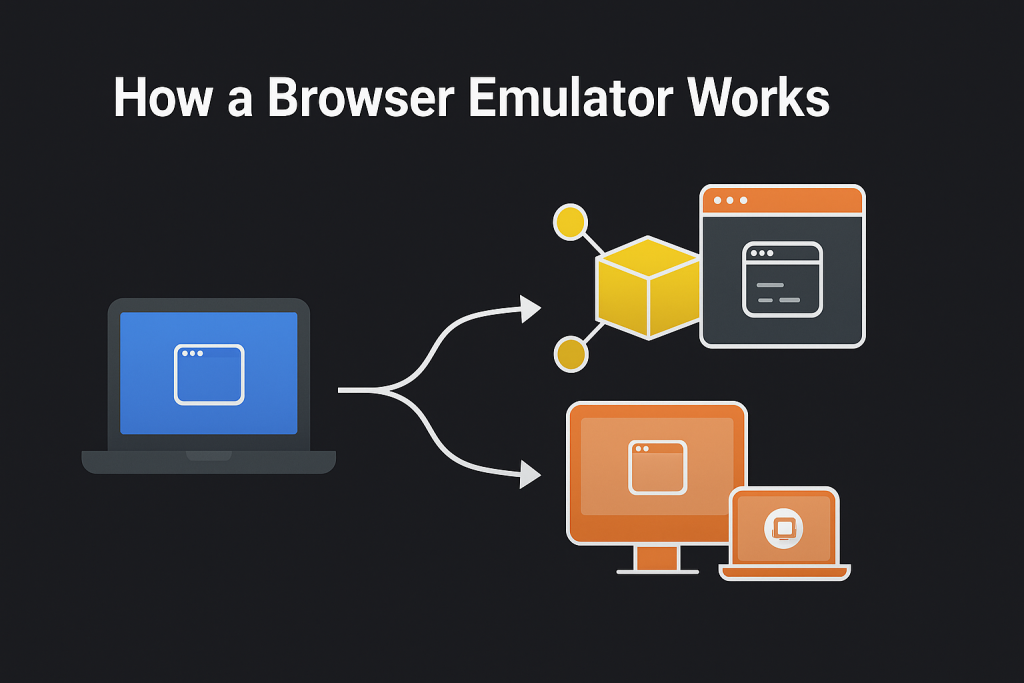
Basically, an online browser emulator provides access to a browser that is not physically installed in your machine. This is usually done by spinning up a virtual machine or a containerized environment – commonly Docker-based – that has the required browser installed. Users then connect remotely, interacting with this web emulator as though it were running locally. All user action is relayed back in real time, causing the illusion that the user interacts locally, whereas the actual browser runs up in the cloud.
While technically this isn’t “emulation” in the strict computer science sense – since you’re accessing a real instance of the browser – it has become common in the industry to call this process a browser emulator. Another implementation involves giving remote access to a physical machine with the required browser installed. Through services like Citrix or third-party remote desktop applications, only the browser’s graphical user interface may be streamed to the tester.
Whether virtualized or hosted on physical hardware, the goal is the same: allowing developers and testers to interact with browsers they might not otherwise have easy access to.
Why is browser emulation needed?
The primary reason developers and QA engineers rely on a web browser emulator is website and web application quality assurance. Since users access sites through a variety of browsers, OSs, and devices, it’s crucial to verify consistent performance across these conditions. An online browser emulator allows testers to simulate the environment without having to install any additional hardware or software.
They visually test the website using an application like Chrome Emulator and Safari Emulator, compare the webpage design with its intended mockup, and confirm that fonts, spacings, colors, and layouts render correctly across the browsers. For functional testing, it’s all about interaction: clicking buttons, filling out forms, running scripts – to ensure that workflows perform as intended regardless of the browser. By using an online web browser emulator, teams save both time and resources while ensuring their product meets professional standards.
Browser emulator test automation
While manual testing is valuable, the most efficient approach involves automating tests with tools like Selenium. QA engineers write scripts simulating user behavior: logging in, filling forms, navigating menus, and so forth, and run these scripts under various browsers using web emulators. Testing against multiple environments is vastly reduced in time due to automation, which also ensures better consistency of results. Usually, browser emulator online services would offer good integration with automation frameworks, so one might easily orchestrate large batches of tests. By integrating automation with browser emulators, companies work on scalable and repeatable testing pipelines that guarantee websites function smoothly in real-world conditions.
Chrome Emulator
As of now, Google Chrome is the world’s most widely used browser, holding a significant share in global markets. Due to this dominance, the Chrome Emulator has had to be an integral tool in quality assurance processes. Testing for the correct look and feel of the web application in Chrome is of utmost priority, since that would cover most of the users. Additionally, Chrome offers powerful developer tools that make it easier to debug and troubleshoot issues, which are often mirrored in browser emulator online services.
Microsoft Edge Emulator
As the default browser on Windows machines, Microsoft Edge represents a major portion of the Windows user base. A Microsoft Edge Emulator allows teams to verify whether their web application works well and correctly in this particular environment. Edge is Chromium-based while still having some distinguishable behavior, so it is essential to ensure compatibility. QA engineers often use web browser emulator services that include Edge among their offerings to ensure that Windows users experience the site as intended.
Safari Emulator
Apple’s Safari browser is the default on macOS, iOS, and iPadOS. Testing with a Safari Emulator ensures that websites display correctly on Apple devices, which dominate the premium device market. For teams that do not have access to any Apple hardware, it would be a great alternative to use an online Mac browser emulator. These emulators allow testers to preview Safari’s unique rendering quirks without needing to own a Mac or iPhone, ensuring cross-platform consistency.
FireFox Emulator
Mozilla FireFox is one of the popular free software alternatives to Chrome and Edge. Its rendering engine is very much different from that of Chromium, bringing about differences in site behavior. Hence, a FireFox Emulator becomes a necessity for checking the compatibility of the said browser with users who cherish privacy and open-source software. Since the highest standards of functioning and accessibility are expected from FireFox users, a web browser emulator that emulates FireFox must be used to make sure that no segment of the user base is left behind.
Online web browser emulator services
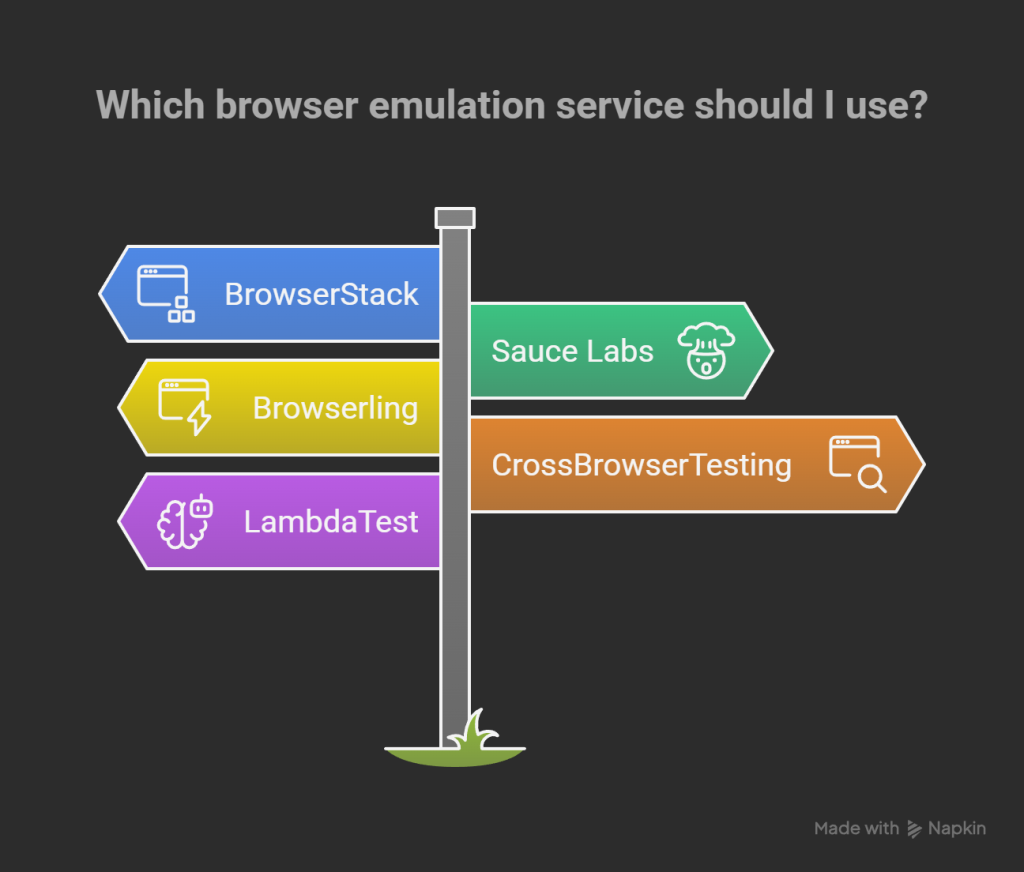
There are quite a few platforms that offer full browser emulation services online:
BrowserStack – offers hundreds of real devices and browsers for both manual and automated testing.
Sauce Labs – cloud-based testing with perfect CI/CD pipeline integration for automation.
Browserling – lightweight live interactive browser testing directly from your own browser.
CrossBrowserTesting – visual and automated testing into thousands of browsers and devices.
LambdaTest – numerous browser and OS combinations at affordable pricing with parallel execution.
Conclusion
Today, an online web browser emulator is one of the most practical tools for web designers and QA engineers. These services, from Chrome Emulators to Firefox Emulators to Mac browser emulators, ensure that the websites work well across all devices and platforms. Manual checks supplemented with automated testing accomplish fast, reliable, and thorough cross-browser coverage for teams.